Chains play a pivotal role in various transport systems, facilitating the smooth movement of goods, materials, and products. Their ability to efficiently transport cargo and motion makes them indispensable in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and automation.
In this article, we will talk about into four different types of chains used in transport systems: accumulation chains, flat double chains, chains with attachments, and stainless-steel chains. We will compare their advantages and disadvantages to provide insights into their suitability for different applications.
Accumulation Chains:
Accumulation chains are designed to temporarily halt or accumulate products along a conveyor line. They are commonly used in scenarios where items need to be synchronized, accumulated, or stopped for a certain period of time during the production process. These chains consist of specially designed rollers or friction segments that allow products to accumulate without causing damage.
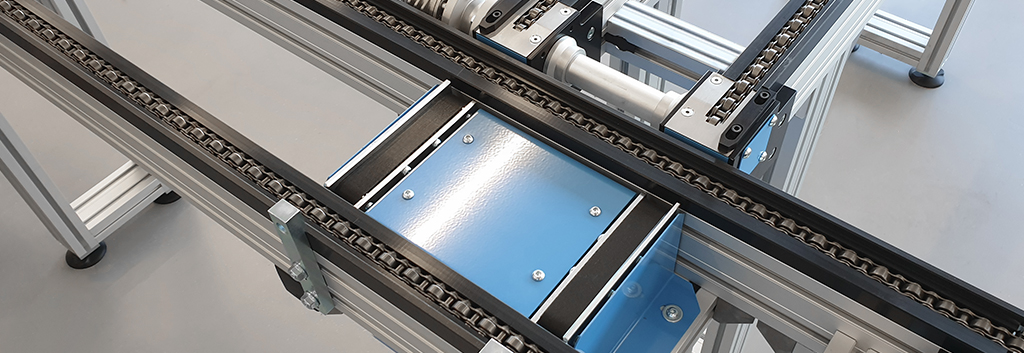
Advantages:
- Synchronization: Accumulation chains enable controlled and synchronized movement of products, preventing collisions and congestion in the conveyor system.
- Flexible Production: They are well-suited for processes that require intermittent stopping or accumulation, contributing to better production flow.
- Damage Prevention: Products are less likely to get damaged due to controlled accumulation.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Speed: Accumulation chains may have limitations in terms of speed due to the intermittent nature of their operation.
- Cost: The added features and components can lead to a higher initial cost.
Flat double Chains:
Flat double chains are characterized by their flat, wide surface area. They are commonly used in applications that involve the transportation of heavy loads or products with irregular shapes. The flat double design provides stability and a smooth surface for products to move across.

Advantages:
- Load Bearing: Flat double chains excel at carrying heavy loads, making them ideal for industries like automotive manufacturing and heavy machinery.
- Stability: The flat double surface ensures stability for products, preventing tipping or slipping during transport.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Flexibility: The flat top design might limit the flexibility of the chain when navigating curved paths.
- Noise: The interaction between the chain and conveyor components can result in higher noise levels.
Chains with Attachments:
Chains with attachments are designed to accommodate specific tasks within a transport system. These attachments can include hooks, clamps, brackets or specialized components that allow the chain to interact with products in a unique way.

Advantages:
- Precision: Chains with attachments provide precise control over product orientation and movement.
- Task Specific: Attachments are tailored to specific tasks, making them suitable for industries with unique handling requirements.
- Automation: These chains play a crucial role in automated systems, where consistent and controlled actions are essential.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: They may have a complex design, leading to increased maintenance and potential points of failure.
- Cost: Customized attachments and the specialized nature of these chains can contribute to higher costs.
- Limited Applicability: Chains with specific attachments might not be easily adaptable to different tasks or products.
Stainless Steel Chains:
Stainless steel chains are known for their corrosion resistance and durability. They find applications in industries where hygiene, cleanliness, and resistance to environmental factors are crucial, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.

Advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel chains can withstand harsh environments, including exposure to water, chemicals, and high temperatures.
- Hygiene: These chains are easy to clean and maintain, making them suitable for industries with strict hygiene standards.
- Longevity: They have a longer lifespan compared to regular chains, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Stainless steel chains are more expensive to manufacture and purchase than traditional carbon steel chains.
- Weight: The higher density of stainless steel can result in heavier chains, which might limit their use in certain applications.
- Lower Strength: Stainless steel chains generally have lower tensile strength compared to their carbon steel counterparts.
In conclusion, the choice of chain in a transport system depends on various factors, including the specific application, load requirements, environmental conditions, and budget considerations. Accumulation chains offer controlled accumulation, flat top chains excel in load-bearing capacities, chains with attachments provide task-specific solutions, and stainless-steel chains prioritize corrosion resistance and hygiene. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and a thoughtful analysis of these factors will aid in selecting the most suitable chain for a given transport system scenario.


